INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE IMAGING(RADIOLOGY)
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), although occasionally used to encompass a variety of infective and purely inflammatory bowel conditions, usually refers to two idiopathic conditions: Crohn disease ulcerative colitis Indeterminate colitis is added to the list and represents ~6% of inflammatory bowel disease cases 2.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Colon Case Studies CTisus CT Scanning
A perianal fistula is an abnormal connection between the epithilialised surface of the anal canal and the skin. Obstruction of anal gland which leads to stasis and infection with absces and fistula formation (most common cause). Inflammatory bowel diseases (Crohn's disease more common than colitis ulcerosa)
The Radiology Assistant Bowel wall thickening CTpattern
The purpose of this paper is to evaluate the role of imaging in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including detection of extraluminal complications and extraintestinal manifestations of IBD, assessment of disease activity and treatment response, and discrimination of inflammatory from fibrotic strictures.. Radiology. 2006; 238:517-530.
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE IMAGING(RADIOLOGY)
Sensitivity of MRI for the number of affected bowel segments was 97.5% with a specificity of 100%, whereas ultrasound scored 76% and 75%, respectively. For stenosis, MRI had a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 96%, and ultrasound a sensitivity of 58% and specificity of 100%.
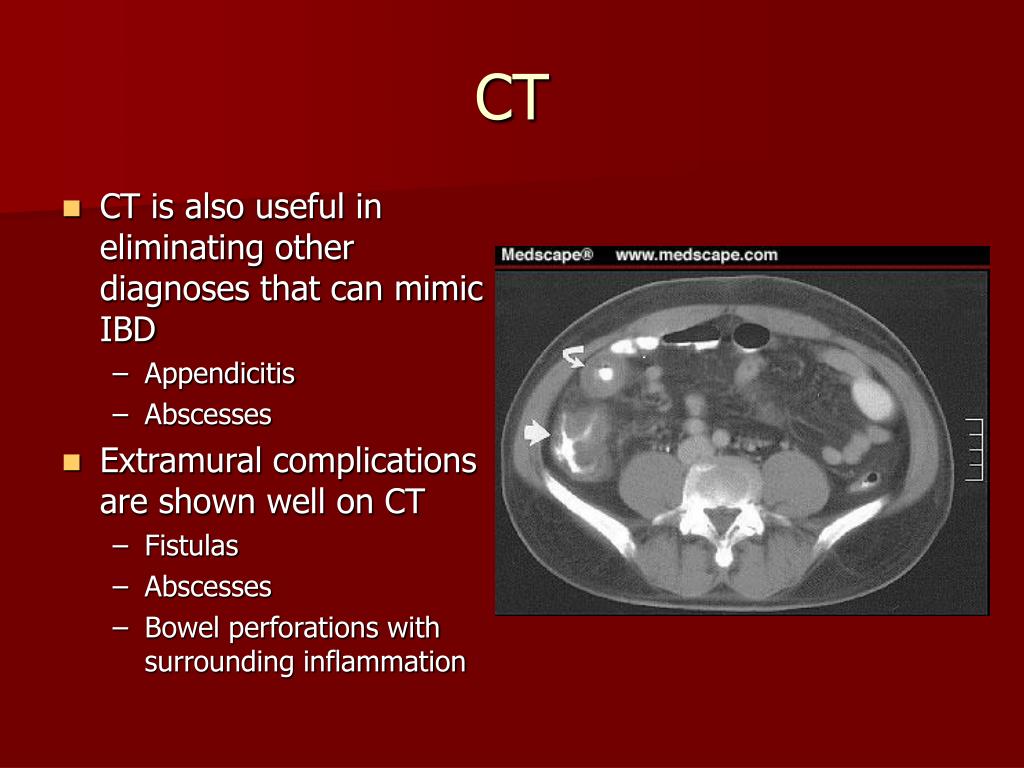
PPT Radiographic Imaging in Inflammatory Bowel Disease PowerPoint Presentation ID6712333
Crohn's disease is a chronic, recurrent inflammation of the bowel wall of unknown origin. The disease has a tendency for transmural progression with ulceration, abscesses, fistula formation, fibrosis and (intermittent) luminal obstruction.

INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE IMAGING(RADIOLOGY)
This article, authored by the Society of Abdominal Radiology Crohn's Disease-Focused Panel, illustrates the imaging findings and recommended radiology report impression statements described in the consensus recommendations with examples of CT enterography and MR enterography images.
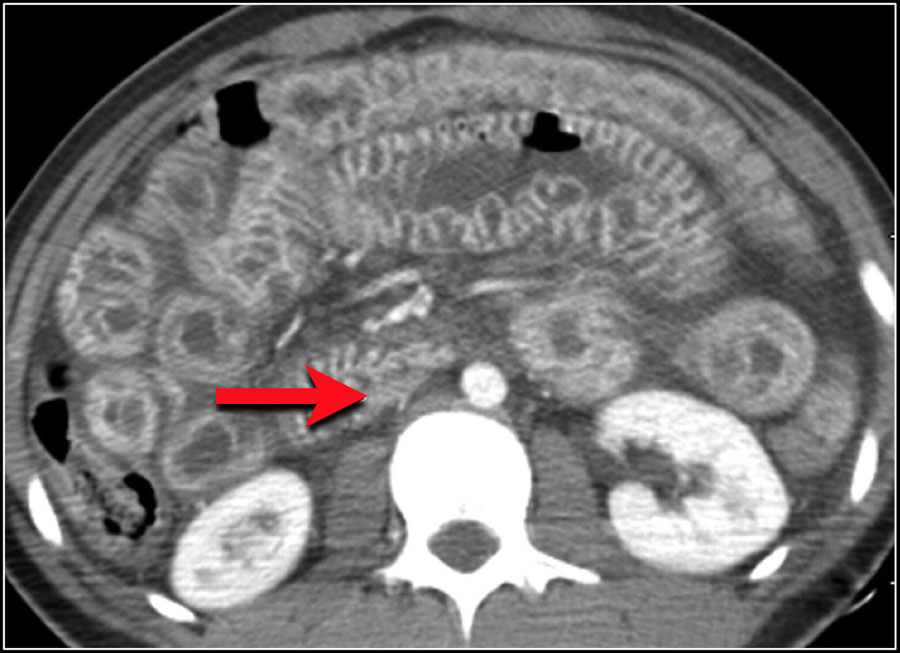
The Radiology Assistant Bowel wall thickening CTpattern
Radiology Crohn's Disease-Focused Panel, the Society of Pediatric Radiology, the American Gastroenterological Association, and other experts, systematically evaluated evidence for imaging findings associated with small bowel Crohn's disease enteric inflammation and established recommendations for the evaluation, interpretation, and

Inflammatory Bowel Disease Body MRI
The use of cross-sectional imaging and ultrasonography has long complemented endoscopic assessment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Clinical symptoms alone are often not enough to assess disease activity, so a reliance on non-invasive techniques is essential. In this paper, we aim to examine the current use of radiological modalities in aiding the management of patients with IBD. We focus.

Inflammatory Bowel Disease in the Emergency Department emdocs
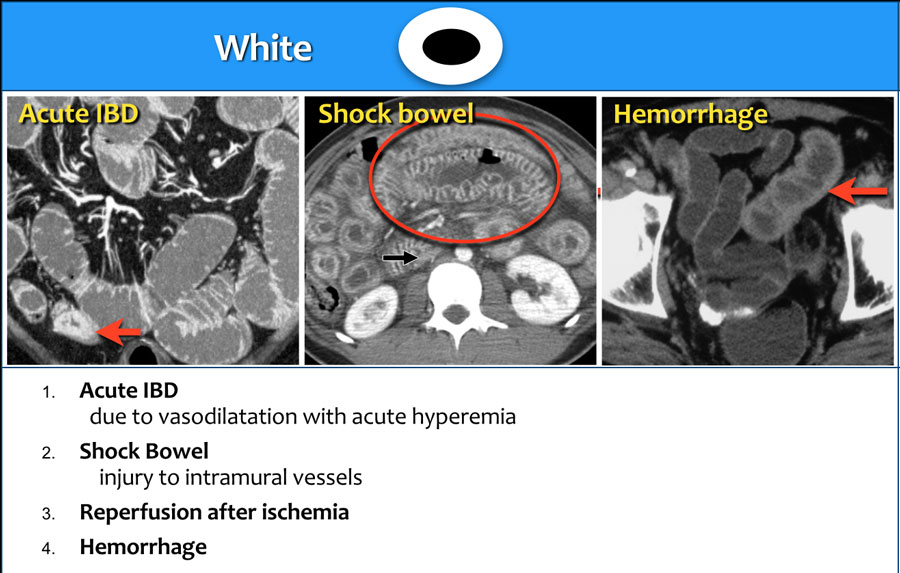
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. The fat halo sign (in colonic imaging) refers to a feature seen on CT abdominal scans, and represents infiltration of the submucosa with fat, between the muscularis propria and the mucosa. It is characterized by an inner (mucosa) and outer (muscularis propria and serosa) ring of enhancing bowel wall.

Inflammatory Bowel Disease Current Role of Imaging in Diagnosis and Detection of Complications
Technical considerations MRI of the bowel (like abdominal MRI in general) is based on the principles of ultra-fast imaging. In the past, most examinations were performed on 1.5T scanners equipped with strong gradient systems. Only recently, bowel MRI on 3T systems has proved feasible. 19

INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE IMAGING(RADIOLOGY)
treatment disease-modifying drugs steroids immunomodulation, e.g. azathioprine, cyclosporine, methotrexate biological agents, e.g. infliximab surgical treatment strictures, fistulae, abscess, perforation non-responding bowel disease, e.g. colectomy Role of imaging Radiology can be useful for diagnosis and follow-up. identify abnormal bowel

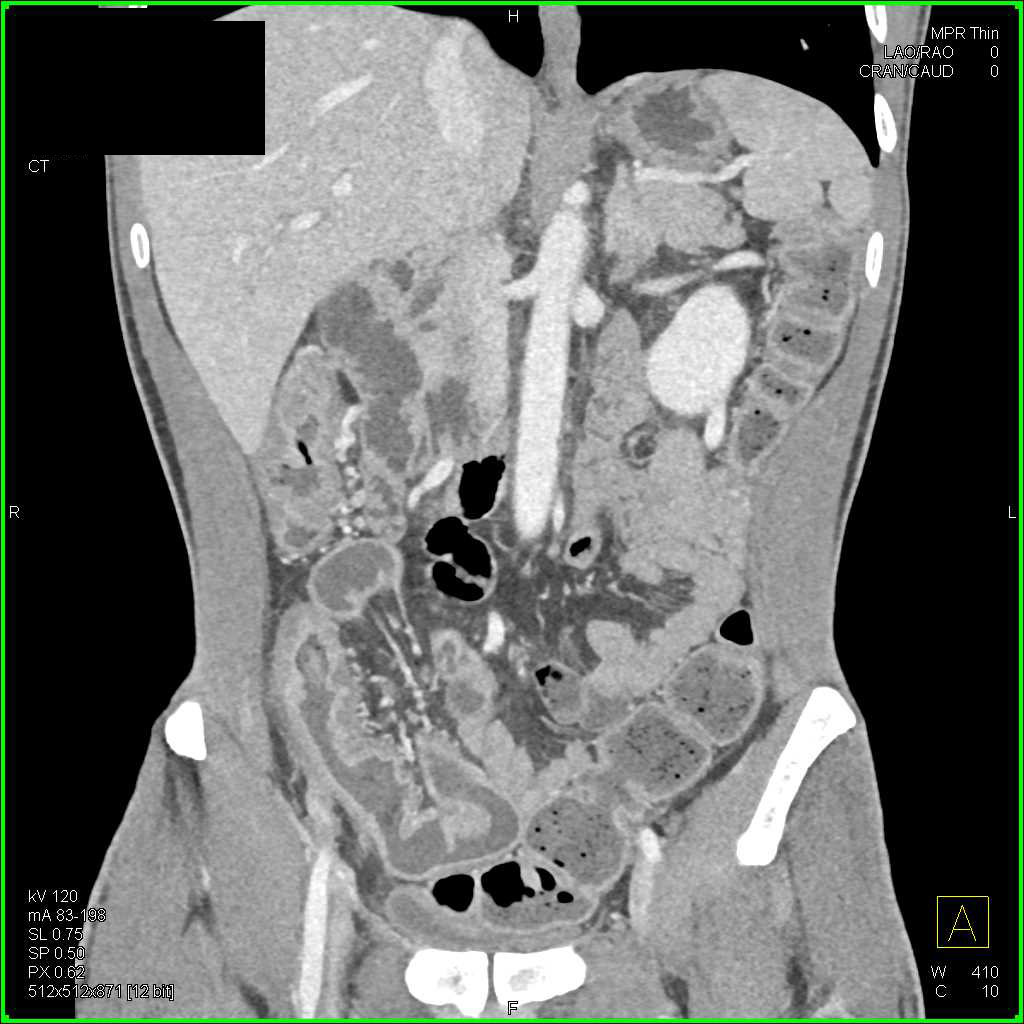
Computed Tomography Enterography and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Abdominal Key
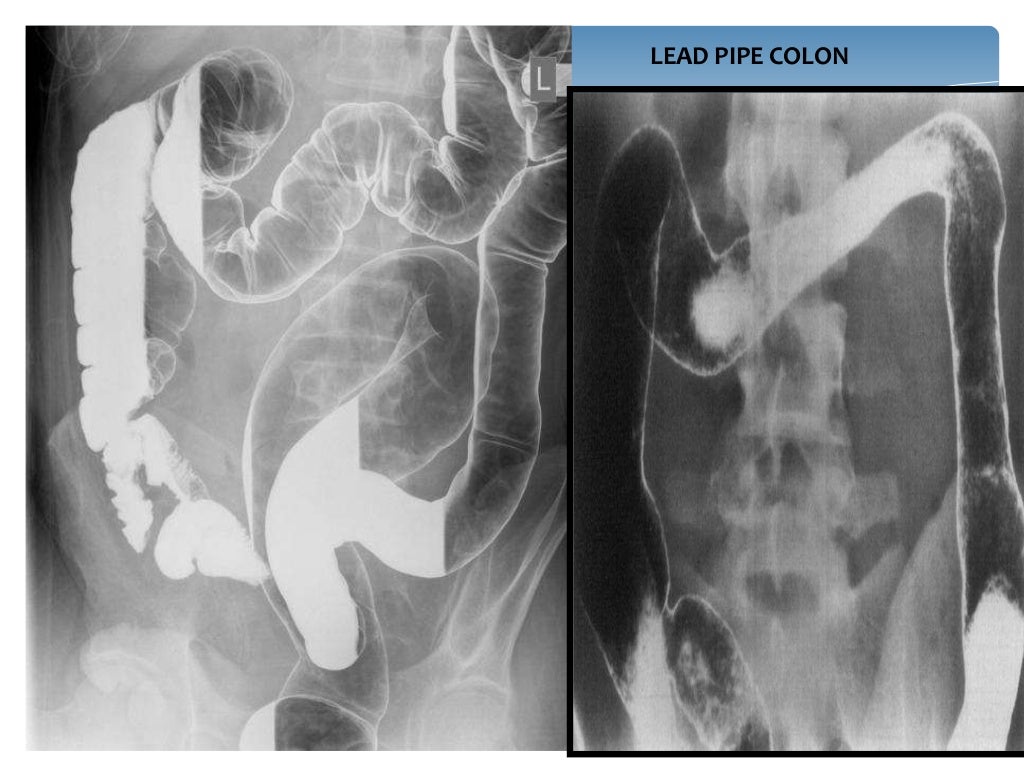
The current status of MRI in ulcerative colitis is that of a promising, non-invasive technique for imaging extent of more severe disease. The most striking abnormalities in ulcerative colitis are colonic wall thickening and increased enhancement. The median wall thickness in ulcerative colitis ranges from 4.7 to 9.8 mm.
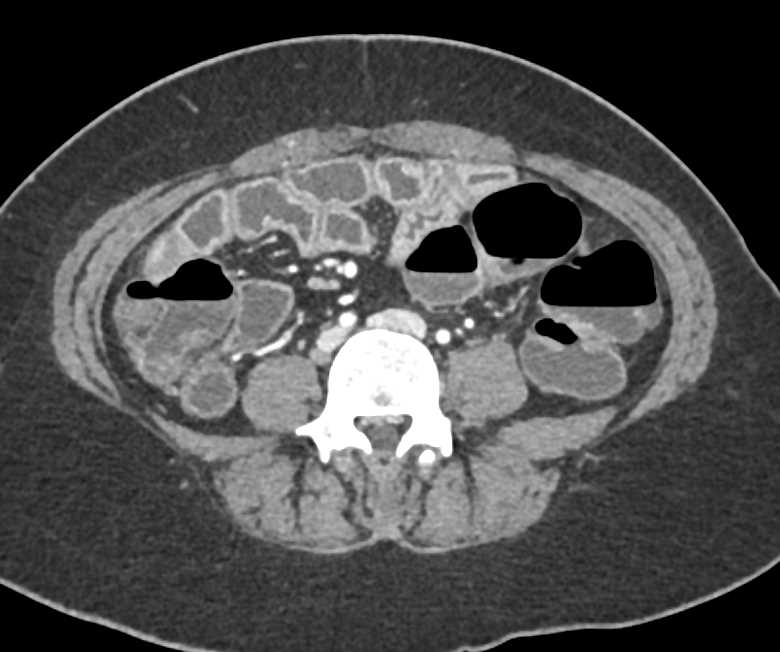
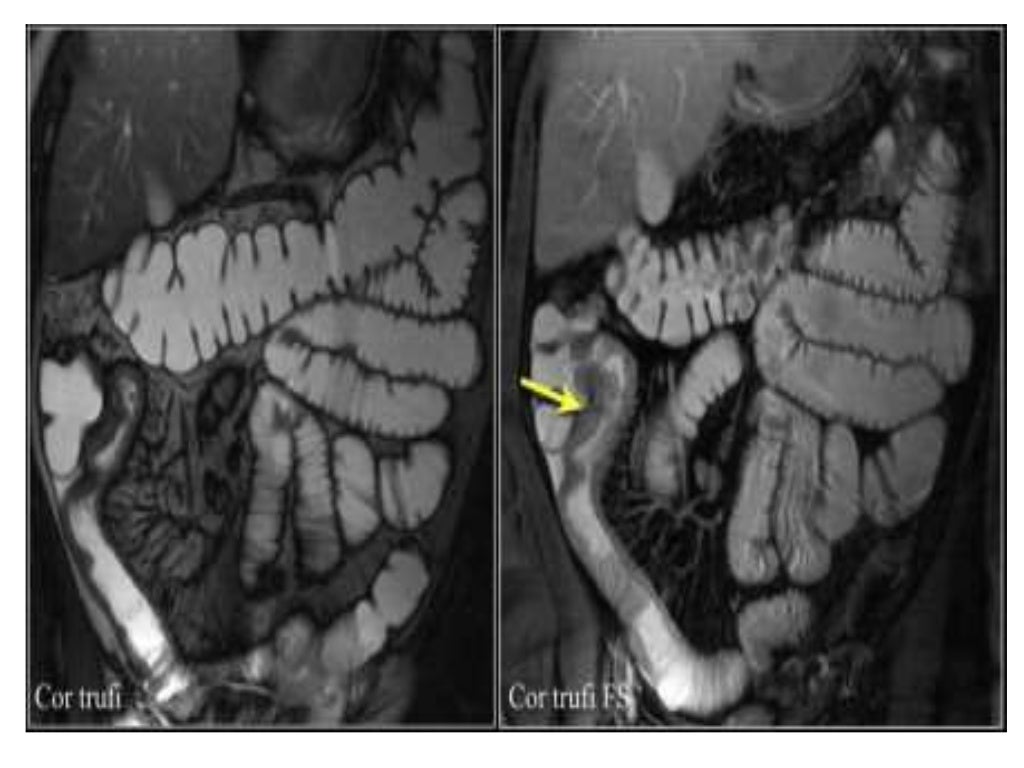
Thickened Small Bowel Loops due to Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Small Bowel Case Studies
Robin Smithuis Alrijne hospital in Leiderdorp, the Netherlands We present 3 videos that will help you to diagnose bowel ischemia with confidence and learn all about closed loop obstruction and the best CT-protocol for patients with an acute abdomen. CT-pattern of Bowel wall thickening Richard Gore and Robin Smithuis

INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE IMAGING(RADIOLOGY)
The current biomarkers used in IBD monitoring are C-reactive protein (CRP) and fecal calprotectin. Based on data from the CALM study, a combination of CRP and fecal calprotectin most accurately predicts relapse ( Lancet 2017;390 [10114]:2779-2789 ). "The CALM study showed that CRP and fecal calprotectin biomarker levels can guide treatment.
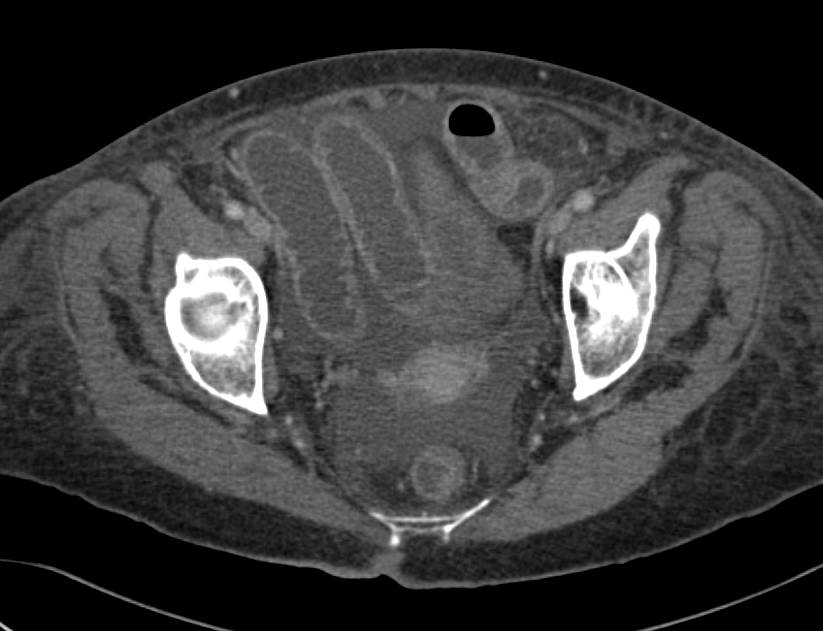
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Small Bowel Case Studies CTisus CT Scanning
Crohn's disease is characterized by inflammatory lesions in the gastrointestinal tract, most commonly in the terminal ileum and colon. The lesions are usually transmural, which can lead to complications like stenoses, fistulas and abscesses.

INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Radiological interpretation for Doctors, Medical students, Nurses
Endoscopic assessment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) can often be imprac-tical and burdensome on both patient and clinician. Complementing endoscopy with radiological imaging has long been established practice in IBD care. With advancements in imaging, there have been great strides in the disease moni-toring and management of IBD. Different